
접근 방법
최소 힙을 구현하는 문제다.
힙(Heap)
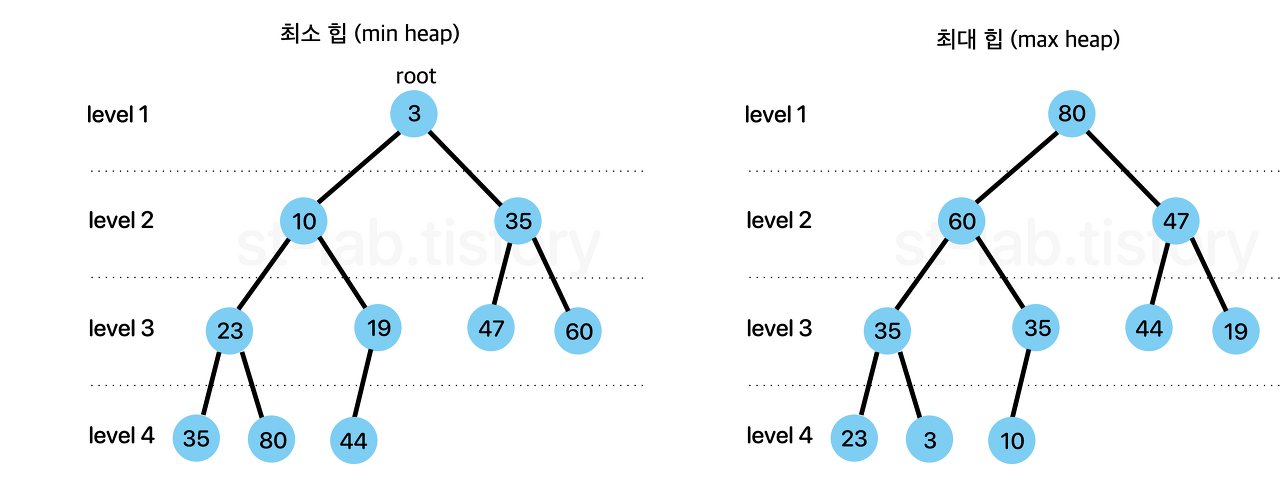
힙은 최댓값 및 최솟값을 찾아내는 연산을 빠르게 하기 위해 고안된 완전이진트리를 이용한 자료구조다. 힙은 부모 노드의 값과 자식노드의 값 사이에 대소관계가 성립한다. 대소관계에 따라 힙에는 두가지 종류가 있는데, 최대 힙과 이 문제에서 구현해야 할 최소 힙이다.
- 최대 힙 : 부모노드의 키값이 자식노드의 키값보다 항상 큰 힙
- 최소 힙 : 부모노드의 키값이 자식노드의 키값보다 항상 작은 힙
키값의 대소관계는 부모노드와 자식노드 간에만 성립하고, 형제 노드 간에는 성립하지 않는다.
힙을 구현할 때는 일반적으로 배열로 구현하게 되는데, 몇가지 특징이 있다.
- 구현의 용이함을 위해 루트 노드의 인덱스는 1 부터 시작한다.
- 왼쪽 자식 노드 인덱스 = 부모 노드 인덱스 x 2
- 오른쪽 자식 노드 인덱스 = 부모 노드 인덱스 x 2 + 1
- 부모 노드 인덱스 = 자식 노드 인덱스 / 2
코드
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
static ArrayList<Integer> heap;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
heap = new ArrayList<Integer>();
heap.add(0);
int n = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int data = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
if (data == 0)
sb.append(del()).append("\n");
else
insert(data);
}
System.out.print(sb.deleteCharAt(sb.length() - 1));
}
public static void insert(int num) {
heap.add(num);
int p = heap.size() - 1;
while (p > 1 && heap.get(p) < heap.get(p / 2)) {
int temp = heap.get(p / 2);
heap.set(p / 2, num);
heap.set(p, temp);
p /= 2;
}
}
public static int del() {
if (heap.size() <= 1)
return 0;
int min = heap.get(1);
heap.set(1, heap.get(heap.size() - 1));
heap.set(heap.size() - 1, min);
heap.remove(heap.size() - 1);
int parent = 1;
while (parent*2 < heap.size()) {
int child = parent * 2;
// 자식 노드 중 더 큰 노드의 값으로 변경
if (child + 1 < heap.size() && heap.get(child) > heap.get(child + 1))
child++;
// 부모 노드가 자식 노드보다 작면 break
if (heap.get(child) > heap.get(parent))
break;
int temp1 = heap.get(child);
int temp2 = heap.get(parent);
heap.set(child, temp2);
heap.set(parent, temp1);
parent = child;
}
return min;
}
}'알고리즘 > Class 3' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 백준 BOJ 1992번 (0) | 2022.08.22 |
|---|---|
| 백준 BOJ 1931번 (0) | 2022.08.22 |
| 백준 BOJ 1780번 (0) | 2022.08.20 |
| 백준 BOJ 1764번 (0) | 2022.08.19 |
| 백준 BOJ 1697번 (0) | 2022.08.19 |




댓글